Ascomycin
Ascomycin Specification
| Appearance | Amorphous white powder | Standard Packing | 10g/bag or per customer request | |
| Purity (HPLC) | 95% | Inventory | Normally we have Ascomycin in stock | |
| Total purity | < 5% | |||
| Melting point | 156 - 161 °C | Ascomycin physical parameters | ||
| Heavy metal | < 0.002% | CAS No: | 104987-12-4 | |
| Water | < 3.0% | Formula | C43H69NO12 | |
| Total Isomer of Ascomycin | < 5% | Molecular Weight | 792.01 | |
| Synonym | FK520, FR 900520 | |||
| Solubility | Soluble to 50 mM in DMSO and to 50 mM in ethanol | |||
| Structure | 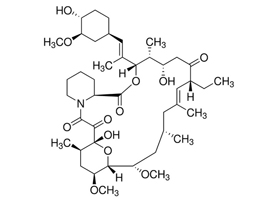 |
|||
| Certificate of Analysis | Ascomycin COA | |||
| Literature | Ascomycin literature | |||
| MSDS | Ascomycin MSDS | |||
| References: | ||||
| 1. | Hatanaka et al (1988) FR-900520 and FR-900523, novel immunosuppressants isolated from a Streptomyces. II. Fermentation, isolation and physicochemical and biological characteristics. J.Antibiot (Tokyo). 41 1593. | |||
| 2. | Motamedi et al (1996) Characterization of methyltransferase and hydroxylase genes involved in the biosynthesis of the immunosuppressants FK506 and FK520. J.Bacteriol. 178 5243. PMID: 8752344. | |||
| 3. | Arndt et al (1999) Secretion of FK506/FK520 and rapamycin by Streptomyces inhibits the growth of competing Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Cryptococcus neoformans. Microbiology 145 1989. PMID: 10463165. | |||
| 4. | Revill et al (2002) Genetically engineered analogs of ascomycin for nerve regeneration. J.Pharmacol.Exp.Ther. 302 1278. PMID: 12183690. | |||
| . | ||||
|
Copyright © 2020 - . All Rights Reserved |
||||